API Responses
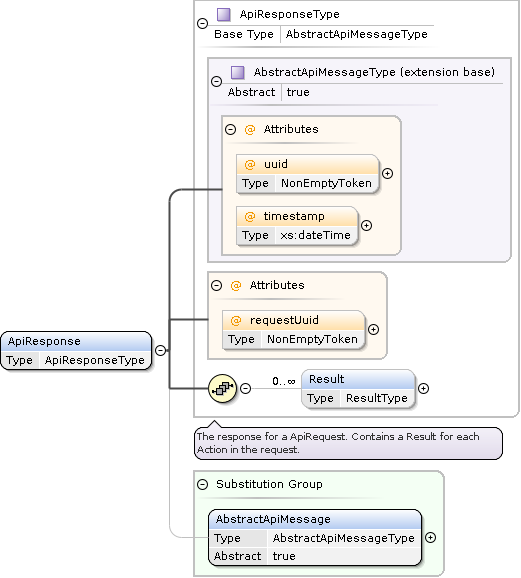
Response Formats
XML Document
Add the Accept: application/xml header to the request to receive XML response format.
ZIP Bundle
Add the Accept: application/zip header to the request to receive ZIP bundle response format.
The ApiResponse will be located in the top-level file /response.xml within the ZIP archive. All additional files bundled in the ZIP will have unique filenames, allowing them to be extracted into the same directory without overwriting previous response contents.
Tip
Utilizing the ZIP format can help minimize both bandwidth and quota consumption.
Tip
To create a unique name for the top-level ApiResponse file, add the filename-dynamic=true query parameter to the primary endpoint URI. For example, using /public/api/v1?filename-dynamic=true will generate a filename like /response-20250210T080835277003937Z-0194eee7-2ccd-7bad-b883-d264f77ed824.xml.
You can also customize the filename prefix with the filename parameter. Moreover, the filename-stamped parameter determines whether a timestamp and response UUID are appended to the filename. For instance, /public/api/v1?filename-dynamic=true&filename=myresponse123&filename-stamped=false will result in the filename /myresponse123.xml.
When filename-dynamic=true is enabled, the filename for the ApiResponse file can also be extracted from the Content-Disposition response header by substituting the .zip extension with .xml.
img and doc Resources
Images and documents retrieved from the secondary endpoints are provided in the format specified by the Content-Type response header.
Response Codes
Status code |
Possible Causes |
|---|---|
401 Unauthorized |
Token expired |
403 Forbidden |
Request Rejected |
429 Too Many Requests |
Quota Exceeded, Too many penalties |
503 Service Unavailable |
User Concurrency Exceeded, System overload |
Response Headers
X-IPI-SUCCESS
The X-IPI-SUCCESS header appears once and contains a boolean value (true or false)
to indicate whether all actions in the processed request were successfully completed.
X-IPI-CONTINUATION-NAME
The X-IPI-CONTINUATION-NAME headers lists the names of the continuation action names present in the response.
This header can occur multiple times, once for each distinct continuation name.
Content-Disposition
The standard Content-Disposition header (MDN)
is used to suggest a filename for the response.
Retry-After
The standard Retry-After header (MDN)
is used in redirect and error responses to specify the appropriate wait time for the client.
It can occur using both syntax variants: <http-date> (e.g. Retry-After: Fri, 7 Mar 2025 07:28:00 GMT) and <delay-seconds> (e.g. Retry-After: 120).
Server-Timing
The standard Server-Timing header (MDN)
is used to report server-side timing information.
Ratelimit-Weight
The Ratelimit-Weight header indicates the number of bytes, formatted as a decimal integer, that have been counted towards the quota for the current response.
X-IPI-PENALTY
The X-IPI-PENALTY header indicates the total count of accumulated penalties, formatted as a decimal integer.
X-IPI-ACQUIRE
The X-IPI-ACQUIRE header reports the ISO 8601 formatted duration (e.g. X-IPI-ACQUIRE: PT5.327691S) which was waited to receive a Request processing permit.
X-WAF-SUPPORT-ID
The X-WAF-SUPPORT-ID header is included for rejected requests with status code 403.
This header contains a token that network administrators can use to determine the reason for the rejection.